|
L'aide française est disponible au format PDF en cliquant ici (ou dans le Menu "Démarrer", Finale 2010, Documentation PDF française)
Le tutoriel français est disponible au format PDF en cliquant ici.
La mise à jour de l'aide française au format HTML sera disponible prochainement.
|
Traduction française :

|
Frequency Modulation Chord Generator Plug-in
How to get there
Select two successive, single notes in one staff with the Selection Tool l. The notes can be of any duration, but must be in layer 1, voice 1. From the Plug-ins menu, choose Scoring and Arranging, Composer’s Assistant, and then Frequency Modulation Chord Generator.
What it does
The Frequency Modulation Chord Generator plug-in creates a new staff with a sequence of chords, each of a whole note duration. A process called Frequency Modulation determines the notes that make up the generated chords. This plug-in was designed to be a compositional tool capable of automatically generating a series of chords with increasing complexity and texture.
Frequency Modulation, in terms of keyboard synthesizers, begins with a simple oscillator called the Carrier (frequency A). The Carrier is then altered in frequency by another oscillator called the Modulator (frequency B). A sound results, with a complex spectrum. This spectrum has energy at certain frequencies:
… A - 3B, A - 2B, A - B, A, A + B, A + 2B, A + 3B …
In this series, frequencies may become negative. In these cases, the absolute (positive) value of the frequency is taken.
The Modulation Index indicates which frequencies from the energy spectrum will be kept.
Index = 1: A
Index = 2: A - B, A, A+B
Index = 3: A – 2B, A - B, A, A+B, A + 2B
Index = 4: A – 3B, A – 2B, A - B, A, A+B, A + 2B, A + 3B
Etc.…
The Frequency Modulation Chord Generator Plug-in converts the two input notes into frequency, based on an equal temperament pitch table (pitches from one octave to the next have a 1:2 ratio, such that any note’s frequency is twice the frequency of the note one octave below; e.g. A4=440Hz and A3=220Hz):
|
MIDI Note Number
|
Pitch
(where middle C equals C4)
|
Frequency (Hz)
|
|
60
|
C4
|
261.626
|
|
61
|
C#4/Db4
|
277.183
|
|
62
|
D4
|
293.665
|
|
63
|
D#4/Eb4
|
311.127
|
|
64
|
E4
|
329.628
|
|
65
|
F4
|
349.228
|
|
66
|
F#4/Gb4
|
369.994
|
|
67
|
G4
|
391.995
|
|
68
|
G#4/Ab4
|
415.305
|
|
69
|
A4
|
440
|
|
70
|
A#4/Bb4
|
466.164
|
|
71
|
B4
|
493.883
|
The frequency of the first input note becomes the Carrier, and the frequency of the second input note becomes the Modulator. These frequencies are entered into the index synthesis algorithm and returned again as MIDI notes. It is these MIDI notes that make up the chords generated.
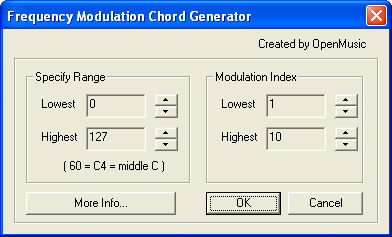
- Specify Range. Because of the multiplications in the synthesis algorithm, the notes of the generated chords could extend far beyond any useful range. Use the Specify Range settings to avoid such extreme pitches.
- Modulation Index. The values chosen for the Modulation Index will determine how many chords are generated, as well as how many notes appear in each chord. The number of chords generated is equal to one more than the Highest Modulation Index minus the Lower Modulation Index (if lowest index is 3 and highest index is 7, then the number of chords generated is 7-3+1 or 5). The number of notes in each chord will generally be one less than twice the modulation index (a chord at Modulation Index 5 will have 5x2-1 or 9 notes). However, due to the nature of frequency modulation calculations, some notes may be duplicated within one chord.
- More Info · Cancel · OK. Click More Info for a reminder of what input this plug-in requires and a brief summary of what the plug-in does. Click Cancel to dismiss the dialog box without making any changes, or Click OK to make the selected changes.


